Research facilities
Microarea X-ray diffractometer
We have several microarea X-ray diffractometers with different specifications.
(Please see the following table for more detail about each device)
R-AXIS BQ: X-ray diffractometer for bone quality evaluation
|
The world’s first X-ray diffractometer dedicated to analyzing bone quality using the preferential alignment of apatite as the evaluation criterion. We have developed this diffractometer in collaboration with Rigaku, a major domestic diffractometer manufacturer in Japan. We can now easily evaluate bone samples by using this diffractometer along with a radiation source such as MoKα that emits X-rays with high penetration power. In addition, it is equipped with transmissive optics such that a two-dimensional detection method for diffraction lines is used with imaging plates. Special data analysis programs for bones have been developed, enabling us to determine numerous bone-quality parameters automatically and non-invasively by simply mounting samples on a stage. Furthermore, X-ray absorption (bone density) and X-ray diffraction (bone quality) can be concurrently measured. |

|
D8 DISCOVER with GADDS Super Speed 6 kW (Rotor): High-intensity X-ray diffractometer with two-dimensional detector
|
This diffractometer employs a powerful X-ray source, the Turbo X-ray Source, using a self-rotating anode, and quicker measurements of smaller areas become possible by utilizing fine-focus high-intensity X-rays. X-ray diffraction data in an ultra-small region of ~φ20 μm can be obtained by focusing incident X-ray beams with a collimator. Moreover, it uses a two-dimensional detector and thus can quickly collect an enormous quantity of two-dimensional data, enabling quick, high-performance, and highly accurate measurements. |

|
D8 DISCOVER with GADDS 3kW (Sealed-tube): X-ray diffractometer with two-dimensional detector
|
Microarea X-ray diffraction information can be obtained by focusing incident X-ray beams with a collimator. Moreover, it uses a two-dimensional detector and thus can quickly collect an enormous quantity of two-dimensional data, enabling quick, high-performance, and highly accurate measurements. |
|
M18XHF22-SR: Microbeam X-ray diffractometer
|
In X-ray diffractometry, the wave nature of X-rays along with the knowledge that X-ray wavelengths are close to the spacing between planes in the crystal surface can be used to analyze the crystal structures of materials through the observation of diffraction (interference) phenomena by irradiating X-rays onto materials. This diffractometer focus irradiated X-rays with a collimator and microarea X-ray diffraction information can be obtained. |

|
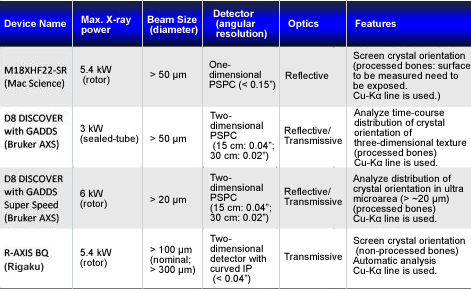
Specifications of X-ray Diffractometers
XCT Research SA+: pQCT bone densitometer for animal experiments
|
Volumetric bone density (mg/cm3) in the cross section of bone is analyzed using X-ray computed tomography (CT) technology. |

|
SMX-100CT: Microfocus X-ray CT system
|
This CT system uses a cone-beam X-ray CT system and a high-performance computer to perform three-dimensional image processing, producing various types of images including three-dimensional images, arbitrary partial cross-sectional images, and transmission images. |

|
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
|
X-rays with two different wavelengths are irradiated onto the whole body and the areal bone density (mg/cm2) is determined from the differences in transmittance of these two types of X-rays. |

|







