最新情報
最新の30件
2026.02.20
【招待講演】中野先生が、第364 回塑性加工シンポジウム「積層造形技術の最新動向とモノづくりへの活用」で講演しました。
中野貴由:積層造形の基礎から応用と産官学連携の取り組み、2026 年2 月20 日(金)10:00~10:40、エル・おおさか 708会議室[大阪市中央区北浜東3-14]
会告はこちら
テキストはこちら
2026.02.17
【論文】Materials Today Communicationsにおいて、バイオメディカル応用に向けた高抗菌性Ti-Mo-Cu合金の開発に関する研究成果がOA論文として掲載されました。
Yichun Zhu, Qiang Li, Hu Zhao, Xuyan Liu, Hao Wang, Masaaki Nakai, Kenta Yamanaka, Mitsuo Niinomi, Ryosuke Ozasa, Takayoshi Nakano:
Development of Ti-Mo-Cu alloys with enhanced antibacterial activity for biomedical application, Materials Today Communications, 51 (2026) 114868.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2026.114868
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
To advance the performance of Ti alloys for biomedical applications, Cu--a β-stabilizing element--was incorporated into a Ti-Mo alloy to synergistically achieve desirable mechanical properties and enhanced antibacterial activity. Ti-6Mo-(0, 1, 3, 5, 7)Cu ingots were fabricated via high-vacuum non-consumable arc melting, followed by homogenization treatment and hot rolling into sheets. Specimens for characterization and testing were cut from the sheets and subsequently solution-treated. Phase composition was analyzed using X-ray diffraction, and microstructure was observed by optical microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Mechanical properties were determined via conventional tensile test, while superelasticity was evaluated through cyclic loading-unloading test. Corrosion resistance was assessed by potentiodynamic polarization measurement, and antibacterial activity was investigated using E. coli and S. aureus as the test strains, with commercially pure Ti serving as the control group. The results demonstrate that Cu addition enhances β-phase stability, inducing a phase composition shift from α'- and α''-phases to a dominant β-phase. Stress-induced martensitic transformation was observed in the Ti-6Mo-7Cu alloy, which exhibited a superelastic recovery rate of up to 2.4 %. All Ti-Mo-Cu alloys displayed self-passivation behavior, with a passivation current density below 12.00 µA·cm⁻². The released Cu²⁺ concentration was approximately 6.94 µg·L⁻¹ after 24 h of immersion in PBS, while it reached ∼23.44 µg·L⁻¹ after 168 h of immersion--meeting the biosafety requirements. Antibacterial efficiency was greatly improved with increasing Cu content. Specifically, the Ti-6Mo-7Cu alloy achieved antibacterial rates of 90.6 % and 79.8 % against E. coli and S. aureus, respectively, making it a promising candidate for biomedical applications.
Keywords
Ti-Mo-Cu alloys; Microstructure; Superelasticity; Corrosion resistance; Antibacterial activity
2026.02.17
【卒論】卒業論文発表会が行われました。
中野研の8名(太田 魁君、小倉 拓巳君、柴田 凌君、永野 登基君、西岡 心之介君、溝上 翔太君、横山 凌大君、渡邊 亮太君)が卒業論文発表をしました。B4の皆さん、お疲れさまでした。
2026.02.10
【論文】Materials Transactionsに電子ビーム積層法により作製した NiTi コーティングの組織進化および耐摩耗性向上に関する論文が受理されました。
Lei Wang, Masayuki Okugawa, Yuheng Liu, Ken Cho, Hiroyuki Y. Yasuda, Takayoshi Nakano, Yuichiro Koizumi: Microstructural evolution and wear resistance enhancement of electron-beam-fabricated nickel titanium coatings on titanium by heat treatment, Materials Transactions, (2026), in press.
2026.02.09
【修論】修士論文発表会が行われました。
中野研の7名(内芝 旭祥君、菊川 泰地君、重永 徹平君、清水 佑太君、船奥 和真君、宮澤 啓太郎君、山野 大陸君)が修士論文の発表をしました。M2の皆さん、お疲れ様でした。
2026.01.31
【特別講演】中野先生が、第47回東北骨代謝・骨粗鬆症研究会(共催:旭化成ファーマ)にて特別講演を行いました。
中野貴由:骨質指標としての骨基質配向性と骨粗鬆症をはじめとする骨疾患による変化
2026年1月31日(土)17:45〜18:45、TKPガーデンシティPREMIUM仙台西口(8F)
プログラムはこちら
2026.01.28
TCTJAPANで中野先生がパネリストとして、AMの明るい未来を語るとともに、NTTザムさんのブースを訪問しました。
2026.01.26
【論文】Trans Tech Publications発行の Materials Science Forum において、レーザ粉末床溶融結合法(LPBF)を用いた耐火系高エントロピー合金(Refractory HEA)の in situ 合金化に関する研究成果が掲載されました。
Yong Seong Kim, Ozkan Gokcekaya, Ryosuke Ozasa, Takayoshi Nakano:
In situ Alloyed Refractory High Entropy Alloy by Laser Powder Bed Fusion, Materials Science Forum, 1175 (2026) 105-110.
DOI: 10.4028/p-0OnKo3
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
Pre-alloyed powders, which are mainly used in laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), have the disadvantage of being time-consuming and costly to manufacture. To overcome these disadvantages, in-situ alloying, which mixes pure element powders and performs alloying in real time during the LPBF process, has been attracting attention. In particular, it is quite challenging to manufacture high entropy alloy (HEA) containing high melting point refractory elements by in-situ alloying. In this study, we designed a single-phase BCC refractory HEA with a mix of Ti, Nb, Mo, Ta, and W through thermodynamic calculations and fabricated the designed composition by LPBF by mixing powders of each element and performing in-situ alloying. High energy density and remelting effectively suppressed segregation of constituent elements, which caused a decrease in residual stress and increased relative density. Our study represents a pioneering attempt to manufacture in-situ alloyed HEA by LPBF and demonstrates the effectiveness of in-situ alloying using mixed powders.
2026.01.25
【論文】Trans Tech Publications発行の Materials Science Forum において、積層造形(AM)で作製した IN718 ニッケル基超合金の階層的組織構造が力学特性に及ぼす影響に関する研究成果が掲載されました。
Kippei Yamashita, Ken Cho, Takuma Saito, Taisuke Sasaki, Katsuhiko Sawaizumi, Masayuki Okugawa, Yuichiro Koizumi, Takayoshi Nakano, Hiroyuki Y. Yasuda:
Influence of Hierarchical Structure on Mechanical Properties of Additive Manufactured IN718 Alloys, Materials Science Forum, 1175 (2026) 129-134.
DOI: 10.4028/p-1DlHhB
Abstract
Selective laser melting (SLM) can produce Ni-based superalloys with a unique hierarchical structure consisting of micrometer-scale crystallographic lamellar microstructure and nanometer scale cellular structure under optimized process parameters. This work investigated the effects of input energy density on the morphology of the cells and its influence on the tensile properties of Ni based superalloy prepared by SLM. We found that the cell spacing decreases with decreasing input energy density. Further investigation of the cells clarified that the boundary of cells is a low angle grain boundary with dislocation cell wall and segregation of certain elements such as Nb and Ti. Moreover, it was demonstrated that the boundary of cells performs as a significant barrier to the griding dislocation. Thus, the cell boundary leads to strong strengthening through the Hall-Petch law.
2026.01.25
【論文】Trans Tech Publications発行の Materials Science Forum において、Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Mo 系バイオ高エントロピー合金(bio-HEA)の微細組織とヤング率の関係に関する研究成果が掲載されました。
Mitsuharu Todai, Nagi Takahashi, Neiro Tanaka, Daisuke Tanaka, Takeshi Nagase, Aira Matsugaki, Takayoshi Nakano:
Microstructure and Young's Modulus of (TiZr)₂₋ₓ(NbTaMo)ₓ Bio-High Entropy Alloys, Materials Science Forum, 1175 (2026) 85-90.
DOI: 10.4028/p-ZmAnP4
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
In recent years, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) have attracted significant attention owing to their remarkable physical properties such as high strength. It has also been reported that HEAs have a high potential as biomaterials. Bcc-type bio-HEAs possess high strength and biocompatibility equivalent to those of pure titanium. Bio-metallic materials require a low Young's modulus, similar to that of natural bone, but the Young's modulus of bio-high entropy alloys has not yet been clarified. Therefore, this study elucidates the relationship between microstructure control and Young's modulus in titanium-based bio-HEAs. The TiNbTaZrMo-based bio-HEAs were composed of two bcc phases. These two phases correspond to dendrite and interdendrite structures, respectively. In this study, it was found that by varying the volume fractions of these two phases, it is possible to control the Young's modulus.
2026.01.15
【記事】Science Portal および Yahoo!ニュースに、「高さ25.36センチの東京スカイツリー 3Dプリンターで内部の柱まで再現 阪大」の記事が1月15日に掲載されました。
★高さ25.36センチの東京スカイツリー 3Dプリンターで内部の柱まで再現 阪大、Science Portal、2026年1月15日
★高さ25.36センチの東京スカイツリー 3Dプリンターで内部の柱まで再現 阪大、Yahoo!ニュース、2026年1月15日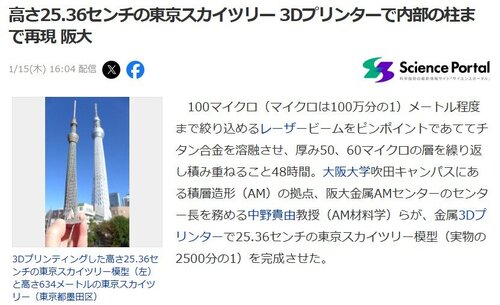
2026.01.14
【報告書】JST-CRDSから「研究開発の俯瞰報告書・ナノテクノロジー・材料分野~領域別動向編~(2026年)| 社会インフラ・モビリティ応用」が本日公開されました。
「研究開発の俯瞰報告書 ナノテクノロジー・材料分野」はこちらから
→https://www.jst.go.jp/crds/report/CRDS-FR-N.html
構造材料はこちら
2026.01.13
【受賞】M2清水佑太さんが、一般社団法人スマートプロセス学会学術奨励賞の受賞が決定しました。表彰式は次回学術講演会です。
清水佑太:L-PBFによる微細組織制御を介したインバー合金の低熱膨張化、(一社)スマートプロセス学会・学術奨励賞、(2026).
2026.01.10
【PJ】JST-Crestナノ力学中野チームの研究推進会議を1月9日、10日の2日間、KKRホテル名古屋で行いました。
有意義で充実した会議となりました。ご準備いただいた、君塚先生、さらには参加いただいたメンバーの皆様に御礼申し上げます。
2026.01.07
【動画配信】中野研を中心に開発したUNIOS PLスペーサーに関する記事と動画が掲載されました。
「金属AM技術を用いた脊椎治療向けインプラントの開発で患者の負担削減を期待」
記事はこちら
動画はこちら
2026.01.05
【解説】自動車技術(Vol. 80, 2026年1月号)に中野先生、石本先生による金属AMに関する解説が掲載されました。
中野貴由、石本卓也:自動車産業に向けた金属AMにおける形状・金属組織を活用した力学機能設計、 自動車技術(Journal of Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan)、Vol.80, (2026), 106-112.
PDFはこちら
2026.01.01
明けましておめでとうございます。本年も大きな飛躍の年とすべく、中野研究室一同一丸となって教育・研究活動に邁進してまいります。引き続きご指導のほど、何卒よろしくお願い申し上げます。
2025.12.28
【論文】Materials TransactionsにAl-Si合金の超昇温・超急冷に関する論文が受理されました。
Masayuki Okugawa*, Yuya Furushiro, Seori Motoyama, Yuheng Liu, Takayoshi Nakano, Yuichiro Koizumi: Manuscript number Integrated computational and experimental study on rapid heating and cooling in powder-bed fusion of Al-Si hypoeutectic alloys, Materials Transactions, (2026), in press.
2025.12.19
【行事】2025年度忘年会を開催しました。
中野研究室のメンバーで忘年会を行いました。
皆さん今年もありがとうございました!
2025.12.17
【論文】Journal of Materials Research and Technologyに金属AM(PBF-LB/M)で造形されたステンレス鋼の陽電子消滅による格子欠陥の同定に関する論文がOA論文として掲載されました。
Masataka Mizuno*, Masaki Otsuka, Kazuhisa Sato, Takuya Ishimoto, Takayoshi Nakano, Hideki Araki: Identification of lattice defects in laser powder bed fusion-fabricated 316L stainless steel by positron annihilation spectroscopy, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, in press, 40, (2026), 188-193.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2025.12.147
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
The laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process often introduces lattice defects, such as vacancies and dislocations, within the fabricated materials because of large thermal gradients and rapid cooling rates. In this study, lattice defects in LPBF-fabricated 316L stainless steel (SS) were quantitatively evaluated using positron annihilation spectroscopy, a sensitive technique for detecting and characterizing vacancies and dislocations. The number of lattice defects increased with the LPBF scan speed. Vacancy concentrations and dislocation densities were determined using component analysis of the positron lifetime spectra. The measured vacancy concentration was comparable to the thermal equilibrium concentration of vacancies at the melting point. Additionally, both vacancy concentration and dislocation density increased with scan speed. The increase in dislocation density in the fabricated 316L SS with increasing scan speed of the LPBF process was confirmed using transmission electron microscopy. This study enables the detection and identification of defects in 316L SS under various temperature conditions, offering insights into the performance of 316L SS across a wider range of operating temperatures.
2025.12.14
【論文】Journal of Materials Research and Technologyに金属AM(PBF-LB/M)で造形されたステンレス鋼の陽電子消滅による格子欠陥の同定に関する論文がOA論文として受理されました。
Masataka Mizuno*, Masaki Otsuka, Kazuhisa Sato, Takuya Ishimoto, Takayoshi Nakano, Hideki Araki: Identification of lattice defects in laser powder bed fusion-fabricated 316L stainless steel by positron annihilation spectroscopy, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, in press, (2025).
2025.12.13
【国際会議】Materials Research Meeting 2025(@パシフィコ横浜,12月8日〜13日)に参加しました。
【Session】
Solidification Microstructure in Ti-V Alloy and Ti1(NbMoTa)2W0.5 Alloy Formed under Rapid Cooling via Laser Irradiation
〇Ryosuke Ozasa, Masayuki Okugawa, Kazuhisa Sato, Yuichiro Koizumi, Takayoshi Nakano
Hydrogen embrittlement behavior of Ni-based alloy fabricated by Laser-powder bed fusion
〇Ozkan Gokcekaya, Tatsuya Nitomakida, Takayoshi Nakano
Regulation of mesenchymal stromal cell differentiation by periodic grooved structures fabricated via metal additive manufacturing for the sustainable construction of oriented bone matrix
〇Tadaaki Matsuzaka, Aira Matsugaki, Takayoshi Nakano
【Poster】
Elimination of the 3DP-introduced specific microstructural features and isolation of their strengthening effects
〇Taichi Kikukawa, Takuya Ishimoto
Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Ti-42Nb Alloy Developed via Laser-Powder Bed Fusion
〇Keitaro Miyasawa, Ryosuke Ozasa, Daisuke Egusa, Eiji Abe, Masakazu Tane, Takayoshi Nakano
Bone Matrix Anisotropy as a Novel Indicator of Osteoporosis-related Fragility
〇Taichi Isoya, Aira Matsugaki, Takayoshi Nakano
2025.12.04
【論文】Journal of Physics: Conference Seriesにレーザ粉末床溶融法で作製した β型Ti-Cr 合金における格子欠陥の陽電子消滅分光および第一原理計算による解析に関する論文が掲載されました。
Masataka Mizuno, Ryosuke Takahagi, Ryosuke Ozasa, Takayoshi Nakano, Hideki Araki:
Investigation of lattice defects in β-type Ti-Cr alloys fabricated via laser powder bed fusion using positron annihilation spectroscopy and first-principles calculations, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 3149, (2025), 012010.
DOI: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/3149/1/012010
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
The structure of β-type titanium alloys with a body-centered cubic (BCC) arrangement is stabilized by β-stabilizing elements. In the present study, to clarify the influence of β-stabilizing elements on the stability of lattice defects in β-type Ti-18.7 at%Cr alloys prepared by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), the as-fabricated samples were subjected to positron lifetime measurements. The positron lifetime of the as-fabricated sample was approximately 20 ps longer than that of the annealed sample, indicating the introduction of lattice defects in the as-fabricated samples. The positron lifetime of the defect component in Ti-18.7%Cr fell between those of vacancies and dislocations, suggesting that both types of defects were introduced during LPBF fabrication. In contrast, in the authors' previous study, no lattice defects were observed in Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al, plausibly because of the recovery of vacancies during LPBF cooling. This recovery is attributed to the anomalously fast vacancy diffusion in the BCC β-phase. In the case of Ti-18.7 at%Cr, such vacancy recovery may be inhibited by the presence of Cr atoms, which tend to increase the energy for vacancy formation and migration at neighboring sites.
2025.12.04
【書籍】中野先生と松垣先生が分担執筆した『界面制御による革新的生体適合性材料開発』が2025年12月15日に発刊されます。
高井まどか、三浦佳子、中野貴由、松垣あいら(分担):
界面制御による革新的生体適合性材料開発、株式会社エヌ・ティー・エス、2025年12月15日発刊、ISBN: 978-4-86043-782-4
https://www.nts-book.co.jp/item/detail/summary/bio/20251200_330.html
2025.11.27
【受賞】第19回 物性科学領域横断研究会にて、M2の宮澤君が最優秀若手奨励賞を受賞しました。
レーザ粉末床溶融結合を利用した準安定β型Ti合金の窒素固溶化と高機能化
○宮澤 啓太郎、小笹 良輔、中野 貴由
最優秀若手奨励賞、東京大学、2025年11月27日
2025.11.25
【論文】ElsevierのBioactive Materials (IF=20.3)に水和水に基づく骨組織とハイドロキシアパタイトの接着に関する論文がOA論文として掲載されました。
Shichao Xie, Masahiro Okada*, Haruyuki Aoyagi, Akihisa Otaka, Xiaofeng Yang, Takayoshi Nakano, Takuya Matsumoto*:
Robust adhesion between solid-state hydroxyapatite and bone tissue through surface demineralization, Bioactive Materials, 57, (2026), 632-645.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.11.030
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
Objective Current bone adhesives typically lack adequate mechanical strength, long-term stability, or biocompatibility. To address these limitations, we designed a new adhesion strategy using a solid-state hydroxyapatite (HAp) adhesive in combination with bone surface demineralization.
Methods
Solid-state HAp adhesives were synthesized via wet chemical precipitation and heat treatment. Cortical bone specimens were partially demineralized with phosphoric acid (H3PO4) or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR). Shear adhesion strength of HAp to demineralized bone was measured over time. In vivo fixation was assessed in rats using micro-computed tomography and histology. Statistical analysis used Tukey-Kramer tests after normality and variance checks.
Results
Although the HAp adhesive failed to adhere to non-demineralized bone, effective adhesion was achieved on the surface-demineralized bone tissue. Shear adhesion strength was significantly higher in EDTA-treated samples (238.4 kPa at 10 h) compared to H3PO4-treated samples (102.9 kPa at 1 h), with performance correlating with demineralization depth. ATR-FTIR and SEM analyses revealed that EDTA preserved collagen's triple-helix structure and free water content, both enhancing adhesion. Animal experiments confirmed stable fixation of HAp adhesive to demineralized bone tissue.
Conclusions
Surface demineralization enabled strong adhesion of the solid-state HAp adhesive to bone by exposing collagen swollen with water. Adhesion strength was influenced by structural changes in the demineralized layer, and the adhesive provided stable in vivo fixation, supporting its potential for bone-anchored biomedical applications.
2025.11.19
【論文】ElsevierのBioactive Materials (IF=20.3)に水和水に基づく骨組織とハイドロキシアパタイトの接着に関する論文が受理され、OA論文として掲載予定です。
Shichao Xie, Masahiro Okada*, Haruyuki Aoyagi, Akihisa Otaka, Xiaofeng Yang, Takayoshi Nakano, Takuya Matsumoto*: Robust adhesion between solid-state hydroxyapatite and bone tissue through surface demineralization, Bioactive Materials, accepted, (2025).
2025.11.14
【冶金杯】令和七年度冶金杯ソフトボール大会で優勝しました。
中野研究室が令和7年度冶金杯ソフトボール大会で優勝しました。
来年もチーム一丸で連覇を目指して頑張ります!

2025.11.12
【新聞】日刊工業新聞に、経済産業省による「金属積層造形の普及拡大・活用促進に向けた検討会」の記事が11月11日に、JST-Crestの安田研を中心とした成果が11月12日に掲載されました。
★金属積層造形後押し、経産省産業振興策など検討会、日刊工業新聞、総合2面、
2025年11月11日朝刊
★金属3D積層で高強度、ニッケル基超合金阪大が力学機能制御法、日刊工業新聞、科学技術・大学面、
2025年11月12日
2025.11.12
【委員会】経済産業省による非公開開催の「金属積層造形の普及拡大・活用促進に向けた検討会」の詳細が経済産業省のHPで公開されました。中野先生が委員長を務めています。第一回は2025年10月31日に開催されました。
検討委員会HP→
https://www.meti.go.jp/policy/mono_info_service/mono/sokeizai/AM-WG.html
第一回検討委員会(2025年10月31日)→https://www.meti.go.jp/policy/mono_info_service/mono/sokeizai/AM-WG01.html
★趣旨・目的
積層造形(以下、AM:Additive Manufacturing)は製造業に変革をもたらすと言われてきました。現時点でも、航空宇宙、医療機器、プロトタイプの試作、エネルギーなどの分野で、AMは既に商業的な利用が開始されるなど、AMの利用は拡大しています。
また、経済安全保障の観点でも、AMは、我が国の製造業の優位性、国際競争力を維持するための「ものづくり基盤技術」の一つとして期待されています。
こうした状況を踏まえ、次の点を中心に現状の取組を整理した上で、AMの普及拡大・活用促進に向けて取り組むべき事項に関して検討を行い、具体的な提言を取りまとめる予定です。
AMの価値・可能性
AM人材の確保・強化
AMの技術進展、コスト低減
AMに関する産学連携の強化(地域拠点化を含む)
技術基盤(品質保証・認証制度等)の整備と促進
AMの認知度向上(AM活用事例を含む)
過去の情報
- 2026年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2025年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2024年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2023年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2022年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2021年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2020年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2019年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2018年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2017年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2016年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2015年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2014年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2013年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2012年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2011年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2010年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2009年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2008年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月