最新情報
最新の30件
2025.07.11
【解説】山陽特殊製鋼技報第32巻(2025年6月発行)に中野先生のAMによる金属材料の高機能化に関する寄敲が掲載されています。
中野貴由:
積層造形(Additive Manufacturing)による 金属材料の高機能化、
山陽特殊製鋼技法 特集:部品製造プロセスの革新に寄与する材料技術、 (2025)、Vol.32 No.1、pp.3~24.
https://www.sanyo-steel.co.jp/technology/images/pdf/32/32_03.pdf
2025.07.02
【論文】バイオフィルムに関する研究が、Transactions of the IMF (YTIM)にOA論文として掲載されました。
Hideyuki Kanematsu*, Shochiku Kure, Risa Kawai, Hidekazu Miura, Takayoshi Nakano:
Antibiofilm Potential of Graphene-Dispersed Alkoxysilane Coatings:
A Materials Science Perspective, Transactions of the IMF (YTIM),
The International Journal of Surface Engineering and Coatings, (2025).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00202967.2025.2520667
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
This study investigates the antibiofilm properties of alkoxysilane-based coatings incorporating dispersed multilayer graphene powder. Graphene, synthesised via a proprietary method, was incorporated into a resin matrix at various concentrations (0.1%, 0.5%, and 1.0% by weight) and applied to glass substrates. Raman spectroscopy confirmed the presence of defect-rich, multilayer graphene, which is known to enhance antimicrobial surface properties. Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus epidermidis was evaluated using ISO 4768-standardised crystal violet staining. Results indicated that biofilm development was effectively suppressed at concentrations up to 0.5%, whereas an unexpected increase was observed at 1.0%, possibly due to graphene aggregation and reduced surface exposure. The findings suggest that both graphene concentration and dispersion quality critically influence antibiofilm efficacy. The study highlights the dual role of graphene, both as a physical and chemical antibacterial agent, and its potential application in medical, industrial, and hygienic materials. Further investigation is warranted to optimise dispersion and explore microbial-material interactions in real-world conditions.
Keywords
Graphene-dispersed coatings; alkosysilane resin; biofilm suppression; crystal violet assay; Raman spectroscopy
2025.06.30
【学会】中野研究室のメンバーが THERMEC2025(@University of Tours, France, 6月30日~7月4日)に参加します。
2025/6/30
Invited Speaker
〇Design of high entropy alloy with suppressed elemental segregation for laser powder bed fusion process
Ozkan Gokcekaya, Yong Seong Kim, Takayoshi Nakano
Invited Speaker
〇Electron Microscopy Studies on Orientation-Controlled 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel
Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Kazuhisa Sato, Shunya Takagi, Satoshi Ichikawa, Takuya Ishimoto, Takayoshi Nakano
2025/7/1
Keynote Speaker
〇Innovative design of crystallographic textures and macroscopic shapes via metal additive manufacturing
Takayoshi Nakano
Poster presentation
〇Unique Hierarchical Structural Features Introduced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Their Contribution to Mechanical Function in IN718
Taichi Kikukawa, Takuya Ishimoto, Tsuyoshi Mayama, Ryosuke Ozasa, Takayoshi Nakano
Poster presentation
〇Microstructural Control of Unstable Beta-Type Titanium Alloy Through Powder Bed Fusion Using a Laser-Beam of Metals
Keitaro Miyasawa, Ryosuke Ozasa, Daisuke Egusa, Eiji Abe, Masakazu Tane, Takayoshi Nakano
Invited Speaker
〇Elastic properties of laser powder bed fusion processed β-phase Ti alloys
Masakazu Tane, Shota Higashino, Eisuke Miyoshi, Takuya Ishimoto, Takayoshi Nakano
Invited Speaker
〇Microstructure control of TiAl alloys using peculiar thermal history of additive manufacturing
Ken Cho, Hiroyuki Y. Yasuda, Masao Takeyama, Takayoshi Nakano
〇Novel cellular structure with phase-separation induced dislocation-network in Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Zr high entropy alloy fabricated by laser powder bed fusion
Daisuke Egusa, Han Chen, Ryosuke Ozasa, Masayuki Okugawa, Taisuke Sasaki, Takuya Ishimoto, Koizumi Yuichiro, Takayashi Nakano, Eiji Abe
Poster presentation
〇Spinodal Decomposition and Magnetic Properties of Single-Crystal-Like Fe-Cr-Co Alloy Fabricated by Laser-Powder Bed Fusion Type Additive Manufacturing
Takato Saito, Yuheng Liu, Masayuki Okugawa, Kazuhisa Sato, Takayoshi Nakano, Yuichiro Koizumi
2025/7/2
Invited Speaker
〇A Novel Strategy for the Control of Crystallographic Texture of Metals with Non-Cubic Crystal System via Powder Bed Fusion using a Laser-Beam of Metals
Ryosuke Ozasa, Koji Hagihara, Takayoshi Nakano
〇Discovery of nano-scaled promising strengthening factor in 316L stainless steel fabricated by laser
powder bed fusion
Fei Sun, Yoshitaka Adachi, Kazuhisa Sato, Takuya Ishimoto, Takayoshi Nakano, Yuichiro Koizumi
〇Nano-scaled solidification microstructure characteristics in additively manufactured 316L stainless steel
Fei Sun, Yoshitaka Adachi, Kazuhisa Sato, Takuya Ishimoto, Takayoshi Nakano, Yuichiro Koizumi
〇Influence of hierarchical structure on mechanical properties of additive manufactured IN718 alloys
Kippei Yamashita, Ken Cho, Hiroyuki Y. Yasuda, Takuma Saito, Taisuke Sasaki, Sawaizumi Katsuhiko, Masayuki Okugawa, Koizumi Yuichiro, Takayoshi Nakano
Invited Speaker
〇Growth of Antiphase Domain in Laser-Irradiated Region and Superelasticity of Single-Crystal Like Fe3Al Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
Yuheng Liu, Tsubasa Sato, Masayuki Okugawa, Kazuhisa Sato, Hiroyuki Y. Yasuda, Takayoshi Nakano, Yuichiro Koizumi
2025/7/3
Invited Speaker
〇Additive Manufacturing of Cell-Based 3D Bone-Mimetic Collagen/Apatite Structures
Aira Matsugaki, Takayoshi Nakano
Invited Speaker
〇Control of Bone Microstructure Formation: Role of Soluble Proteins Secreted by Osteocytes
Tadaaki Matsuzaka, Aira Matsugaki, Takayoshi Nakano
2025.06.28
【研究費】中野先生を代表とする、2025年度JSPS科学研究費補助金・挑戦的研究(開拓)が採択されました。
中野貴由:『聴こえる』を制御する骨基質ナノ構造の新奇機能開拓、科学研究費補助金・挑戦的研究(開拓)、2025年度~2027年度、直接経費2000万円(間接経費600万円)
2025.06.28
【学会】第45回日本骨形態計測学会(2025年6月26日~6月28日:埼玉)の表彰式に出席しました。
2025.06.26
【学会】第45回日本骨形態計測学会(2025年6月26日~6月28日:埼玉)に参加しています。
2025.06.25
【新聞】金属3Dプリンターを用いたナノ構造の形成と高強度化に関する記事が日刊工業新聞に掲載されました。
積層合金ナノ構造で高強度 阪大、機能性向上・軽量化に応用
日刊工業新聞 2025年4月11日朝刊29面
2025.06.25
【新聞】日本経済新聞電子版に3Dプリンティングに関する記事が掲載されました。
阪大、金属3Dプリンティング特有の「セル組織」が極めて大きな強化をもたらす原因因子であることを明らかに、日本経済新聞電子版、2025年6月25日 13:37
記事はこちら
JSPSプレスリリースはこちら
大阪大学プレスリリースはこちら
2025.06.24
【論文】【プレスリリース】Materials Research Letters誌に菊川君らが解明した3DプリンティングにおけるInconel 718における強力なセル強化に関する論文がOA論文として掲載されました。同時にプレスリリースし、6月24日14:00に報道解禁になりました。
Taichi Kikukawa, Takuya Ishimoto*, Hyoung Seop Kim, Takayoshi Nakano*:
Remarkable Strengthening Effects of Cells in Laser Powder Bed Fusion Processed Inconel 718,
Materials Research Letters, (2025).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2025.2522801
プレリリースはこちら
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
Alloys fabricated via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) exhibit superior strength. This study investigates the individual strengthening effects of the nanometre-sized cellular and micrometre-sized crystallographic lamellar structures in the LPBF-fabricated Inconel 718 alloy by selectively eliminating these structures through heat treatment and a novel laser scanning strategy, respectively. While cellular structures increased the yield strength by approximately 38%, lamellar structures contributed to only a marginal 2% increase. This finding demonstrates the remarkable strengthening effect of cells on LPBF products. This study highlights that cells are not merely microstructures but are critical features governing the exceptional strength of LPBF products.
Keywords
Laser powder bed fusion; cellular microstructures; lamellar structure; single crystal; strengthening
2025.06.21
【論文】チタン上へのNiTi被膜の電子ビーム造形による耐摩耗性の改善に関する論文がSurfaces and InterfacesにOA論文として公開されました。
Lei Wang, Masayuki Okugawa, Yuheng Liu , Ken Cho, Hiroyuki Y. Yasuda, Takayoshi Nakano, Yuichiro Koizumi:
NiTi coating formation on Ti for enhanced wear resistance utilizing electron-beam additive manufacturing technique,
Surfaces and Interfaces, 72, (2025), 107024; 1-14.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2025.107024
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
Titanium and its alloys are extensively utilized in various industries owing to their high corrosion resistance and excellent strength-to-weight ratio. However, their poor wear resistance limits further applications. The present study developed a novel method to fabricate wear-resistant NiTi coatings on commercially pure titanium (CP-Ti) substrates to overcome this limitation. The process comprises electroplating a pure Ni layer followed by fusion with the CP-Ti substrate by electron beam (EB) scanning. The surface roughness and composition of the coating can be fine-tuned by adjusting the EB irradiation conditions. For example, the average roughness of continuously scanned (CS) coatings is Ra 8.9, while the average roughness of intermittently scanned (IS) coatings is reduced by 60% compared to CS-coatings. Additionally, the Ni concentration in the IS-coatings can be finely adjusted from 45 at.% to 55 at.% by adjusting EB power. X-ray diffractometry (XRD) revealed that IS-coatings are partially composed of superelastic B2-NiTi phases. Nanoindentation and sliding wear tests demonstrated that the hardness-to-modulus (H/E) ratio and depth recovery ratio (ηd,h) of the IS-coating increased by a factor of 4.7 and 2.9 compared to those of CP-Ti, respectively. Additionally, the specific wear rate (Ws) of the IS-coating was reduced by 80% compared to CP-Ti. The mechanical properties of the IS-coating were comparable to those of superelastic NiTi alloy. This newly developed method offers potential applications beyond NiTi coatings, enabling the development of various functional coatings for enhanced wear resistance.
Keywords
Commercially pure Ti; NiTi; Coating; Shape-memory alloy; Mechanial properties; Superelasticity; Wear resistance
2025.06.20
【論文】チタン上へのNiTi被膜の電子ビーム造形による耐摩耗性の改善に関する論文がSurfaces and Interfacesに受理されました。
Lei Wang, Masayuki Okugawa*, Yuheng Liu , Ken Cho, Hiroyuki Y. Yasuda, Takayoshi Nakano, Yuichiro Koizumi*
NiTi coating formation on Ti for enhanced wear resistance utilizing electron-beam additive manufacturing technique,
Surfaces and Interfaces, (2025), in press.
2025.06.19
【論文】Materials Today Communicationsにレーザと電子線で作製したTi合金の力学的・電気化学的特性の異方性に関する論文が掲載されました。
Parinaz Mofazali, Masoud Atapour*, Ozkan Gokcekaya, Sung-Hyun. Park, Batur Ercan, Takayoshi Nakano: Comparison and Evolution of Ti6Al4V Bioalloy Fabricated by Laser and Electron beam Additive Manufacturing: Mechanical Features and Anisotropic Electrochemical Properties,
Materials Today Communications, (2025), 113124: 1-14.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2025.113124
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
With current technology, most biomedical implants are made using metal-based alloys, with a growing preference for metal additive manufacturing (AM) to achieve customized properties. Therefore, this study investigated Ti-6Al-4V (Ti64) alloys produced using two common AM techniques: electron beam melting (EBM) and selective laser melting (SLM). The aim is to compare the microstructure, mechanical properties, and anisotropy electrochemical corrosion behavior of Ti64 samples scanned with SLM-XX, SLM-XY, and EBM-XX strategies. Surface roughness, microstructure, and microhardness tests were conducted to establish correlations with the manufacturing process and surface characteristics. Optical and scanning electron microscopy microstructural analysis revealed notable variations influencing mechanical performance. Moreover, anisotropy-assessing electrochemical corrosion evaluations showed that SLM samples exhibited superior corrosion resistance compared to EBM samples. Notably, the (YZ) planes in the SLM-XY sample demonstrated the highest corrosion resistance (Rct ⁓ 4.45 ×106 Ω.cm2), attributed to reduced dislocation density and enhanced passivation. Furthermore, results showed that the method of fabrication affected the wettability of Ti64 alloys. The SLM-XY samples exhibited the lowest water contact angle (84.45°), whereas the EBM samples showed the highest (99.87°). Finally, bioactivity assessments after 21 days in simulated body fluid (SBF) revealed no cracking or surface damage in any of the tested samples. The formation of calcium- and phosphorus-rich deposits indicates their potential suitability for orthopedic applications.
Keywords
Ti6Al4V; SLM; EBM; Anisotropy; Corrosion; Biomedical
2025.06.17
【論文】Materials Today Communicationsにレーザと電子線で作製したTi合金の力学的・電気化学的特性の異方性に関する論文が受理されました。
Parinaz Mofazali, Masoud Atapour*, Ozkan Gokcekaya, Sung-Hyun. Park, Batur Ercan, Takayoshi Nakano: Comparison and Evolution of Ti6Al4V Bioalloy Fabricated by Laser and Electron beam Additive Manufacturing: Mechanical Features and Anisotropic Electrochemical Properties, Materials Today Communications, (2025), in press.
2025.06.16
【論文】Materials Research Letters誌に菊川君らが解明した3DプリンティングにおけるInconel 718における強力なセル強化に関する論文が受理され、OA論文として掲載されます。
Taichi Kikukawa, Takuya Ishimoto*, Hyoung Seop Kim, Takayoshi Nakano*:
Remarkable Strengthening Effects of Cells in Laser Powder Bed Fusion Processed Inconel 718 Materials Research Letters, (2025), in press.
2025.06.13
【論文】Postecとの共同研究の析出と格子ひずみの競合を利用した高強度・高延性ミドルハイエントロピー合金の国際共同研究が"Materials Science and Engineering A"に掲載されました。
Jae Heung Lee, Hyeonseok Kwon*, Gang Hee Gu, Ji Yeong Lee, Sang Guk Jeong, Emad Maawad, Changwan Ha, Jaemin Wang, Byeong-Joo Lee, Sangbong Yi*, Takayoshi Nakano, Hyoung Seop Kim*:
Harnessing competitive interplay between precipitation and lattice distortion for strong and ductile medium-entropy alloy,
Materials Science and Engineering A, 942, (2025) 148642: 1-11.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2025.148642
論文はこちら
PDFはこちら
Abstract
In Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Mo-C ferrous medium-entropy alloys (FeMEAs), precipitation-driven alteration of matrix composition affects both the kinetics of deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) and the degree of lattice distortion. While DIMT has been well studied, the role of lattice distortion remains explored. In this study, we simultaneously enhance the strength and ductility in Co18Cr13Fe57.5Ni7.5Mo3C1 (at%) FeMEA by harnessing the competitive interplay between precipitation and lattice distortion. Two annealed samples with similar grain sizes but different precipitate characteristics were prepared. The sample with suppressed precipitation exhibits improved ductility while maintaining comparable strength. The two specimens exhibited similar yield strengths due to a trade-off between precipitation strengthening and solid solution strengthening. However, the sample with higher lattice distortion and reduced precipitation demonstrates superior strain-hardening behavior owing to the lattice distortion-induced back stress, acting as an effective strain-hardening mechanism, and delayed DIMT, serving as a ductilizing mechanism. This work offers a strategy to modulate strengthening and deformation mechanisms in Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Mo-C FeMEAs via precipitation control.
Keywords
Ferrous medium-entropy alloy; Precipitation; Deformation mechanism; Strengthening mechanismIn-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction
2025.06.12
【論文】バイオフィルムに関する研究が、Transactions of the IMF (YTIM)に受理されました。
Hideyuki Kanematsu*, Shochiku Kure, Risa Kawai, Hidekazu Miura, Takayoshi Nakano: Antibiofilm Potential of Graphene-Dispersed Alkoxysilane Coatings: A Materials Science Perspective Transactions of the IMF (YTIM), (2025), in press.
2025.06.10
【受賞】中野研究室D1の齊藤光郁さん、森陶子さんが第45回日本骨形態計測学会 若手研究者賞の受賞に内定しました。
齊藤光郁、「抗血液凝固薬投与はオステオカルシンの翻訳後修飾を介して骨基質配向性を変化させる」、2025年6月28日
森陶子、「チタン細線による骨基質配向性制御を介した早期脊椎再建」、2025年6月28日
2025.06.10
【学会】中野研究室のメンバーが日本骨形態計測学会(第45回)(@大宮ソニックシティ、6月27日~6月28日)に参加します。
イブニングセミナー
〇中野貴由、骨質指標としての骨基質配向性の基礎と応用、第45回日本骨形態計測学会、大宮ソニックシティ、2025年6月27日
シンポジウム
〇松垣あいら、基質配向性から見た骨質研究の最前線、第45回日本骨形態計測学会、大宮ソニックシティ、2025年6月27日
〇中野貴由、骨基質配向性を考慮した積層造形による脊椎間スペーサの開発と製品化、第45回日本骨形態計測学会、大宮ソニックシティ、2025年6月27日
一般公演
〇松坂匡晃、松垣あいら、中野貴由、応力刺激に基づく骨基質配向性の制御を介した機能適応、第45回日本骨形態計測学会、大宮ソニックシティ、2025年6月27日
〇松垣あいら、中野貴由、骨基質構造に基づく骨機能再建のための細胞制御マテリアル設計と開発、第45回日本骨形態計測学会、大宮ソニックシティ、2025年6月28日
〇森陶子、松垣あいら、文勝徹、海渡貴司、岡田誠司、中野貴由、チタン細線による骨基質配向性制御を介した早期脊椎再建、第45回日本骨形態計測学会、大宮ソニックシティ、2025年6月28日
〇齊藤光郁、松垣あいら、中野貴由、抗血液凝固薬投与はオステオカルシンの翻訳語就職を介して骨基質配向性を変化させる、第45回日本骨形態計測学会、大宮ソニックシティ、2025年6月28日
〇小笹良輔、中野貴由、妊娠および授乳関連性骨粗鬆症における骨配向性とヤング率の変化、第45回日本骨形態計測学会、大宮ソニックシティ、2025年6月28日
2025.06.09
2025年6月9日 【講演】デンマーク工科大学(DIU)のDorte Juul Jensen教授が訪問し、講演を行っていただきました。最新のμAMプロジェクトの研究に対して議論が盛り上がりました。
デンマーク工科大学(DIU)のDorte Juul Jensen教授が訪問し、講演を行っていただきました。最新のμAMプロジェクトの研究に対して議論が盛り上がりました。


R4 building 2F Seminar Room, Suita Campus, Osaka University
・Microstructural Characterization of Metals in 2D, 3D and 4D
・Microstructural Engineering of Additively Manufactured Metals
Prof. Dr. Dorte Juul Jensen
Technical University of Denmark
2025.06.05
2025年6月5日【訪問】Northeastern UniversityのProf. Xiaoli Zhao先生が中野研を訪問くださいました。
Northeastern UniversityのProf. Xiaoli Zhao先生が中野研を訪問くださいました。
2025.06.05
【論文】Postecとの共同研究の析出と格子ひずみの競合を利用した高強度・高延性ミドルハイエントロピー合金の国際共同研究が"Materials Science and Engineering A"に受理されました。
Jae Heung Lee, Hyeonseok Kwon*, Gang Hee Gu, Ji Yeong Lee, Sang Guk Jeong, Emad Maawad, Changwan Ha, Jaemin Wang, Byeong-Joo Lee, Sangbong Yi*, Takayoshi Nakano, Hyoung Seop Kim*:
Harnessing competitive interplay between precipitation and lattice distortion for strong and ductile medium-entropy alloy,
Materials Science and Engineering A, (2025), in press.
2025.06.01
2025年6月1日・2日 【研究会】いよいよ5年目に入ったJST-Crestのチーム内(大阪大・東京大・熊本大・名古屋大)対面会議を行いました。
いよいよ5年目に入ったJST-Crestのチーム内(大阪大・東京大・熊本大・名古屋大)対面会議を行いました。熱心な議論が繰り広げられました。ご準備いただいた東京大学の先生方、ありがとうございました。
2025.06.01
【学会】日本材料学会第74期学術講演会(@日本大学工学部、5月30日~6月1日)に参加し、以下の発表を行いました。
【オーガナイズドセッション7】(生体・医療材料)
[生体・医療・福祉材料1]
213
レーザ粉末床溶融結合による生体用Ti-42Nb合金の微細組織制御を介した低ヤング率化
◎宮澤啓太郎(阪大),小笹良輔,江草大佑(東大),阿部英司,多根正和(阪大),中野貴由
214
レーザ粉末床溶融結合によるMg-Zn-RE系合金の造形と力学特性解析
◎大川翔(阪大),小笹良輔,徳永透子(名工大),萩原幸司,松本敏治(戸畑製作所),中野貴由(阪大) 日本大学工学部にて
日本大学工学部にて
2025.05.28
【受賞】松垣先生、小笹先生、Gokcekaya先生が粉体粉末冶金協会 2024年度研究進歩賞を受賞しました。 京都大学 宇治キャンパスで授賞式が行われました。
レーザ粉末床溶融結合法による生体用ハイエントロピー合金の新規開発に関する研究
松垣あいら、小笹良輔、Gokcekaya Ozkan
粉体粉末冶金協会 2024年度研究進歩賞

2025.05.20
2025年5月20日 【学会】中野先生が会長を務める(一社)日本Additive Manufacturing学会(日本AM学会)の第一回セミナーが東京で開催されました。
中野先生が会長を務める(一社)日本Additive Manufacturing学会(日本AM学会)の第一回セミナーが東京で開催されました。 現地は定員一杯の約150名の参加、さらにWEBでの150名以上の参加(合計300名以上)があり、大変好評でした。すでに69社の企業賛助会員、約700名の入会となっております。 本セミナーでは、「AM×最先端技術(宇宙・自動車・医療)」を趣旨とし、産学官から多彩な講師陣が登壇し、最新の技術動向や事例紹介、今後の課題などが議論されました。 さらに、参加者同士のネットワーキングの場も設けられ、異分野間の連携促進や技術交流の機会となりました。
2025.05.05
【依頼論文】デンタルインプラントの荷重と骨質に関する論文が、日本補綴歯科学会誌に掲載されました。
黒嶋伸一郎, 中野貴由, 澤瀬 隆:
荷重がインプラント周囲の骨質に与える影響を科学する,
日本補綴歯科学会誌, 17 [2], (2025), 69-76.
https://doi.org/10.2186/ajps.17.69
抄録
本依頼論文は,研究から得られた科学的情報に基づいて,骨質の概念と力に対する骨組織の応答性を正しく理解することであり,著者らが行ってきた骨質に関する一連の基礎的研究と非臨床試験について検討した.その結果,動物種(部位特異性はある)によらず,インプラントに荷重を付与すると,オッセオインテグレーション,骨量,骨密度,骨質が大きく変化した.また,骨質を変化(向上)させるデンタルインプラントの存在が確認できた.したがって,骨質は骨密度とは独立した概念で,同義でもなく類似もしておらず,荷重環境下ではインプラントデザインによりインプラント周囲の骨質が大きく変化することがわかった.
2025.05.01
【解説】まてりあの5月号が発行され、中野先生の本多記念講演の内容の解説記事が掲載されています。
中野貴由:
異方性材料デザインにより材料を主役に~耐熱性金属間化合物から,骨組織,金属3Dプリンティングによる生体材料まで、
まてりあ, 64 [5], (2025), pp. 317-330. (第70回本多記念講演)
http://www.mat.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp/msp6/nakano/a51e100a9d882a8debb79a21ae0abdb9dce8996a.pdf
2025.04.28
【行事】中野研究室恒例の新入生歓迎BBQを行いました。
中野研究室恒例の新入生歓迎BBQを服部緑地公園にて行いました。
OB, OGの方も多数参加していただき、今年も非常に盛り上がりました。
準備してくれたM1の皆さん、ありがとうございました。
2025.04.23
【受賞】齊藤さん、森さんが大阪大学女子大学院生優秀研究賞を受賞しました。
齊藤光郁
薬剤送達によるタンパク質活性化に基づく骨基質配向化制御
森陶子
Tiワイヤを用いた細胞制御による脊椎再建デバイスの創製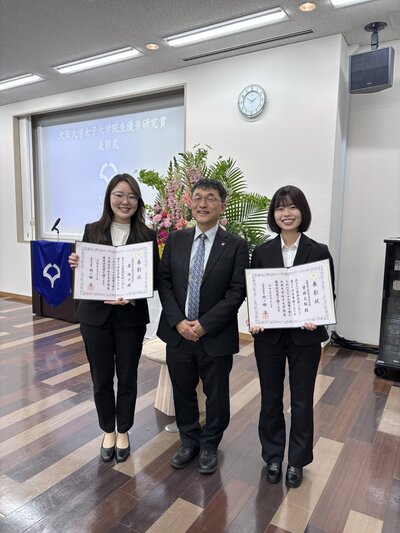
大政工学研究科長とともに
2025.04.17
【受賞記事】日本バイオマテリアル学会誌に大河内賞受賞に関する記事が掲載されました。
第71回(令和6年度)大河内記念技術賞、バイオマテリアルー生体材料―、43 [2], (2025), 176.
PDFはこちら
過去の情報
- 2025年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2024年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2023年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2022年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2021年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2020年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2019年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2018年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2017年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2016年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2015年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2014年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2013年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2012年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2011年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2010年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2009年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月
- 2008年 1月~6月 | 7月~12月